Medical device manufacturing continues to drive the adoption of robot vision to increase throughput, increase yield and reduce the reliance on manual processes. Many production facilities have now turned to collaborative robots which allow operations in medical device production to be taken to the next level of optimisation.
Cobots with vision, tend to work hand in hand with humans balancing the imperative for safety with the need for flexibility and productivity. Robots no longer need to work alone. Collaborative robots are generally designed with inherent safety so they can work alongside humans where possible. Collaborative automation means greater speed and efficiency. Of course, a thorough risk-assessment is still required but the functionality within these robots leads them to be assessed safe once the surrounding conditions and operationality capability are tuned to the safety needs (including any gripper or end-effector design).
Cobots are designed for low payload applications such as handling small parts and inspection tasks so are ideal for medical production processes. Companies continue to look for ways to improve their efficiency by using robot with vision systems, allowing automation of current manual processes to produce productivity gains. Cobots provide a lower price point and lower integration cost to the customer, providing a faster return on investment that unlocks many more industrial tasks for medical device production automation.
Some examples of the current trends in medical device manufacturing for adopting robot vision solutions include:
Machine Tending
Cobot vision removes the need for many operators to be occupied tending to production machinery, feeding and general assembly operations. The cobot can open and close a machine door, pick and place parts for assembly, and even start a machining process by pushing the start button.
Palletising
The ability to stack and un-stack pallets is another requirement, with the vision system providing real-time off-sets and alignment for the pallet stack. A compact robotic cell that accurately loads products onto a pallet, reduces the need for rework while also allowing staff to work safely around the robot. Using cobots with vision within a robot cell allows safe interaction with staff members. Personnel can enter the robot’s operational area to speed up the pallet changes, providing a robotic solution that can work around staff without risking their safety.
Box Erection
Taking flat boxes off a stack and erecting them into a useable format as outer shipper cases is a repetitive and time-consuming action in industry to which cobots with vision are very well suited. Medical device manufacturers need not only to erect the boxes and casings, but print and confirm the serial batch numbers and use by date on the product, all of which can be completed by the same machine vision inspection system.
Functional Repetitive Testing
Manufacturers need to put their products through thousands of hours of test cycling to provide reliability, for example the continued movement of a syringe body or an asthma inhaler valve. Collaborative robots with vision can performs hundreds of hours of testing to support faster testing, improving reliability and quality.
Structured Bin Picking
Parts in a structured position allowing single picks from known datums can be easily completed with cobots and smart vision sensors. Pick and place into a known fixture or position allows integration of such solutions in complex automation production processes.
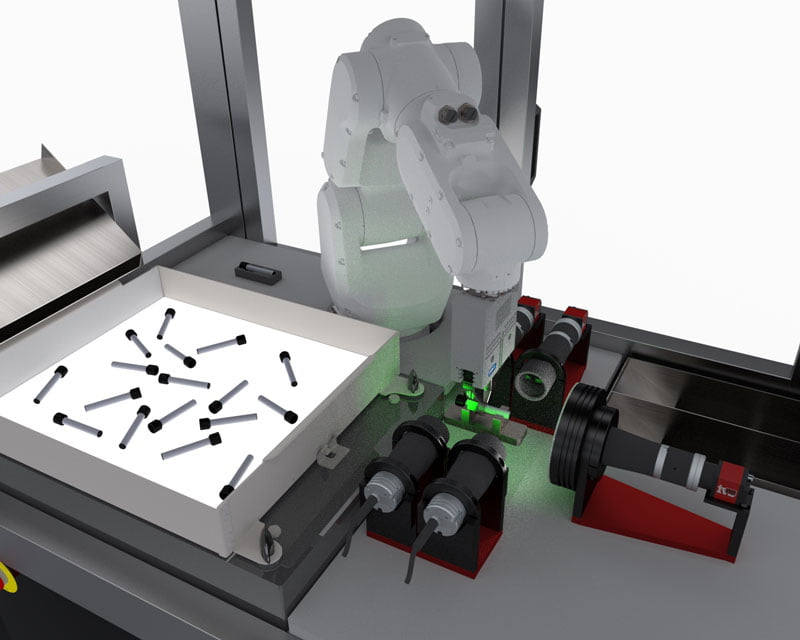
Unstructured Random Bin Picking
Bin picking from a random box of parts can now be accomplished with cobots and 3D vision. A point cloud of known data, identifying individually pickable parts is fed to the robot allowing parts which would have previously required a human picker to now to picked and placed into the next process.
Robots with machine vision will continue to dominate the foreseeable needs for automation of production in medical device manufacturing. With the drive for ever greater flexibility and the need to reduce manpower and increase reliability, this area of automation will continue to be a focus for the medical devices and pharmaceutical industries.